Navigating the Electrical Realm: Ensuring Safety in the Presence of Electricity
Electricity, the lifeblood of modern society, powers our homes, industries, and countless technological advancements. While its benefits are undeniable, electricity also poses inherent risks that can lead to severe injuries, fires, and even fatalities if not handled with utmost care and adherence to safety protocols. Electrical safety, therefore, is paramount in all settings, from domestic installations to complex industrial environments.
Understanding Electrical Hazards: The Spectrum of Risks
Electrical hazards encompass a wide range of potential dangers, each with its unique characteristics and consequences. Some of the most prevalent electrical hazards include:
-
Electrical Shock: The passage of electrical current through the human body, causing a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to cardiac arrest.
-
Electrical Burns: Contact with energized conductors or arcs can cause severe burns, tissue damage, and potential scarring.
-
Arc Flashes: Sudden releases of electrical energy, resulting in intense light, heat, and sound waves, posing a risk of burns, explosions, and secondary hazards.
-
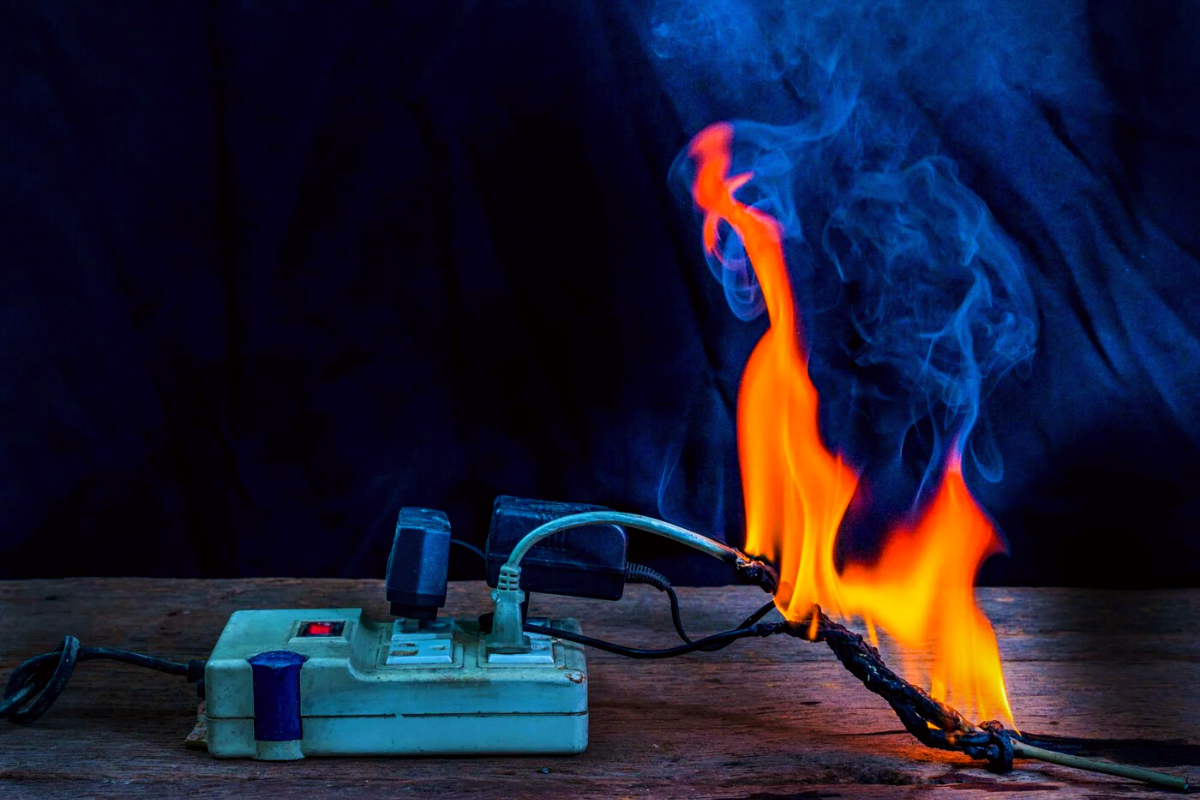
Electrical Faults: Malfunction or damage to electrical equipment can lead to sparks, overheating, and fires.
-
Electrical Explosions: Fumes from overheated insulation or arcing can cause explosions, particularly in confined spaces.
Electrical Safety Standards: A Framework for Protection
To minimize the risks associated with electricity, a comprehensive set of electrical safety standards has been developed. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 70E, also known as the Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace, is the cornerstone of electrical safety in the United States. It provides detailed guidelines for hazard identification, risk assessment, safe work practices, and personal protective equipment (PPE) selection.
Electrical Safety Practices: A Foundation for Prevention
Effective electrical safety practices are essential to prevent accidents and protect individuals from harm. Here are some key principles for electrical safety:
-
De-energization: Always de-energize equipment before working on it to eliminate the risk of electrical shock.
-
Lockout/Tagout: Implement lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization during maintenance or repair work.
-
Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of electrical equipment to prevent electrical shock hazards.
-
Insulation and Guarding: Maintain adequate insulation and guards on electrical conductors to prevent accidental contact.
-
Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain electrical equipment to identify and address potential hazards.
Arc Flash Prevention: Shielding from Explosive Energy
Arc flashes, characterized by intense light, heat, and sound waves, pose a significant risk of burns, explosions, and secondary hazards. Arc flash prevention strategies are crucial in workplaces where arc flash potential exists. These strategies include:
-
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Conduct thorough hazard identification and risk assessment to identify arc flash zones and determine the appropriate level of protection.
-
Arc Flash PPE: Provide and ensure the proper use of arc flash PPE, including arc-rated clothing, gloves, and face shields.
-
Arc Flash Protection Systems: Implement arc flash protection systems, such as arc flash relays and blast-resistant enclosures, to minimize the severity of arc flash incidents.
Global Safety Training: Empowering Electrical Safety
Global Safety Training, a provider of online safety training, offers a comprehensive suite of courses designed to address the diverse electrical safety needs of individuals and organizations across various industries. Our courses are developed by industry experts and aligned with the latest safety standards and best practices. Global Safety Training’s online platform provides a convenient and accessible way for workers to learn about electrical hazards, safe work practices, arc flash prevention, and NFPA 70E requirements.
A Culture of Electrical Safety
Navigating the realm of electricity demands a deep understanding of electrical hazards, a commitment to safe work practices, and a culture of prevention. By investing in comprehensive electrical safety training, individuals and organizations can empower their workforce to work safely around electricity, minimize risks, and create a work environment that prioritizes the well-being of all stakeholders. Remember, electrical safety is not just a responsibility; it’s an investment in a safe and productive future.