Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric Pressure
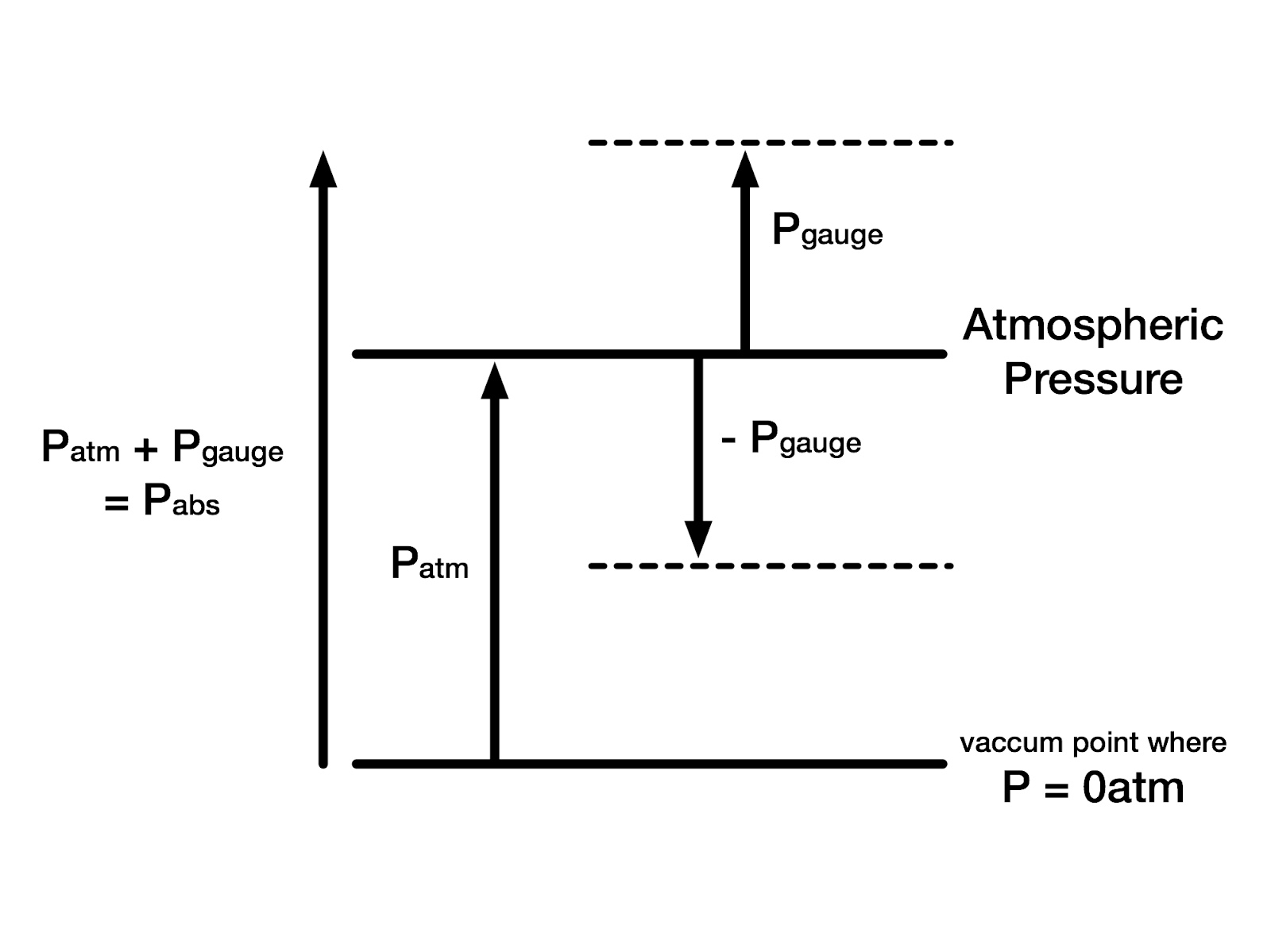
Atmospheric pressure, also called barometric pressure, force per unit area exerted by an atmospheric column (that is, the entire body of air above the specified area). Atmospheric pressure can be measured with a mercury barometer (hence the commonly used synonym barometric pressure), which indicates the height of a column of mercury that exactly balances the weight of the column of atmosphere over the barometer. Atmospheric pressure is also measured using an aneroid barometer, in which the sensing element is one or more hollow, partially evacuated, corrugated metal disks supported against collapse by an inside or outside spring; the change in the shape of the disk with changing pressure can be recorded using a pen arm and a clock-driven revolving drum.
Changes in atmospheric pressure with altitude
